It’s estimated that an average of 8 percent of all commercial rocket launches end in failure.
Multimedia eLearning program by: David A. Johanson © All Rights
David Johanson is a multimedia specialist, CTE instructor and a former Boeing scientific photographer. All content, including photography, graphics and text (unless otherwise noted) was created by the author.
To see an alternative graphic format of this program, please select: ⇒ https://bigpictureone.wordpress.com
Learning objectives Of This Program Includes:
≥ Definition and meaning of space law
≥ History and development of space law
≥ History and development of 20TH and 21ST Century Rocket and Launch disasters
≥ How, where and why rocket launch sites and space portals are located on the globe
≥ Potentially life threatening activities and components of rocket launches —————————————————————————————————————–
.
The Antares 110 rocket engines roared as they illuminated their departure from Earth — seconds later, appearing as if mortally wounded, the multi-staged rocket suddenly lost momentum and sank downward, creating an explosive tower of flames. Over the launch site’s PA system an urgent command required all media personnel to leave their equipment and evacuate immediately. It was reported no deaths had occurred — however the total environmental damage, the launch site cleanup and insurance liability issues are yet to be assessed.
NASA’s video of Antares rocket explosion ⇒http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aL5eddt-iAo
This video shows, press journalist and photographers ordered to evacuate as the Antares rocket explodes and unleashes toxic clouds of vaporized solid rocket propellant. Winds should be blowing to the east, so that burning propellant dissipates over the Atlantic Ocean — not heading west towards potentially populated areas, as is indicated happening in this video. ⇒ http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IclTka711xo
On October 31ST, just three days after Orbital Sciences, Antares rocket launch explosion, Virgin Galactic’s SpaceShipTwo (SS2) disintegrates in an upper altitude reentry over California’s Mojave Desert. Unfortunately the space plane’s pilot was killed, as the remaining components of the craft slammed into an unpopulated area. ⇒http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dy1k5s7Fbl0 ⇒http://www.theguardian.com/science/2014/nov/02/virgin-galactic-spaceshiptwo-crash-investigators-fuel-warnings
Photograph: Kenneth Brown/Reuters
What Goes Up, Must Come Down
Rocket launch projects have always had to contend with laws of physics, in particular, Newton’s law of gravity. Today, these multimillion dollar programs are governed by another set of laws involving multinational, liability space laws. These binding laws are for protecting individuals, communities and the environment from impacts caused by, man-made objects launched into space or subsequent damage of corporate or national operations in space.
 Case Study: The first record of a space law liability occurring was in 1962, on a street within Manitowoc, Wisconsin. Apparently, a three-kilogram metal artifact from the Russian’s 1960, Sputnik 4 satellite launch, reentered the atmosphere unannounced, over an unsuspecting Midwest. The Russian’s denied it was theirs, fearing liability under international law. This event, helped set in motion, the 1963 Declaration on Legal Principals Governing the Activities of State in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space. As an international agreement, it puts forth the responsibility to the State which launches or engages in sending objects into space as internationally responsible for damages caused on Earth. In 1967, the agreement was slightly modified and was titled “Outer Space Treaty 1967.”
Case Study: The first record of a space law liability occurring was in 1962, on a street within Manitowoc, Wisconsin. Apparently, a three-kilogram metal artifact from the Russian’s 1960, Sputnik 4 satellite launch, reentered the atmosphere unannounced, over an unsuspecting Midwest. The Russian’s denied it was theirs, fearing liability under international law. This event, helped set in motion, the 1963 Declaration on Legal Principals Governing the Activities of State in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space. As an international agreement, it puts forth the responsibility to the State which launches or engages in sending objects into space as internationally responsible for damages caused on Earth. In 1967, the agreement was slightly modified and was titled “Outer Space Treaty 1967.” 
A photo illustration of space debris from a low Earth orbit reentering the atmosphere over a city. Earth has water covering 70% of its surface — when attempts fail to guide space debris towards open oceans, the chance for these falling objects to hit a populated area increase. Space Law assesses the liability for damages caused by space debris to the nation or agency responsible for its original rocket launch.
By 1984, the United Nations General Assembly, had adopted five sets of legal principles governing international law and cooperation in space activities. The principles include the following agreements and conventions.”Outer Space Treaty” – the use of Outer Space, including the Moon and other Celestial Bodies (1967 – resolution 2222.) “Rescue Agreement” – the agreement to rescue Astronauts/Cosmonauts, the Return of Astronauts/Cosmonauts and the Return of Objects Launched into Space (1968 – resolution 2345.) “Liability Convention” – the Convention on International Liability for Damaged Caused by Space Objects (1972 – resolution 2777.) “Registration Convention” – the registration of Objects Launched into Outer Space (1975 – resolution 3235.) “Moon Agreement” – the agreement Governing the Activities of States on the Moon and Other Celestial Bodies (1979 – resolution 34/68.)
 Because so many international languages are used for creating these technical agreements — terms and meanings are often misinterpreted. There are linguistic limitations and a general lack of definitions to adequately cover all the specific space concepts and activities using Space Law. Each Nation has its own agenda and vision concerning the development of space, including corporate, cultural and religious interest, adding to the complexity of governing space.
Because so many international languages are used for creating these technical agreements — terms and meanings are often misinterpreted. There are linguistic limitations and a general lack of definitions to adequately cover all the specific space concepts and activities using Space Law. Each Nation has its own agenda and vision concerning the development of space, including corporate, cultural and religious interest, adding to the complexity of governing space.
Although most large “space debris” is monitored with top priority for enabling reentry over uninhabited areas such as oceans and deserts — satellites or sections of rockets still have potential for an unexpected re-entry over an inhabited area. 
Cuba Gives A New Meaning To A Cash Cow
Case Study: In November of 1960, the second stage of a U.S. – Thor rocket fell back to Earth and killed a cow grazing in Eastern Cuba. The final settlement required the U.S. Government to pay Cuba $2 million dollars in compensation — creating the world’s first “Cuban Cash Cow.”
Eventful And Tragic Rocket Launches Associated With Space Exploration
American physicist, Dr. Robert H. Goddard is the father of modern rocket propulsion. Goddard’s published rocket research during the 1920s, is what German military scientist used to help develop the liquid fueled V2 rocket, which terrorized Europe towards the end of WWll. The V2 (technical name Aggregat-4 or A4) rocket was the first human made artifact to leave the Earth’s atmosphere and reach into space. The basic design of modern rockets has changed little in the 100 years since Goddard was awarded a U.S. patent in 1914, for a rocket using liquid fuel.
It’s estimated since the 1950s, of the nearly 8,000 rockets launched into space related missions, 8 percent of rocket launches ended in some-type of failure (2012 spacelaunchreport.com.) The resulting anomalies have cost the lives of hundreds of individuals, including; astronauts, cosmonauts and civilians, along with billions of dollars of property and payload losses. Here’s an abbreviated list of dramatic and tragic events associated with rocket launch failures.

A modified V-2 rocket being launch on July 24, 1950. General Electric Company was prime contractor for the launch, Douglas Aircraft Company manufactured the second stage of the rocket & the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) had major rocket design roles & test instrumentation. This was the first launch from Cape Canaveral, Florida.
Vanguard TV3, December 6, 1957 launched from Cape Canaveral, Florida (U.S.) was the first U.S. attempt at sending a satellite into orbit. A first event of its kind to use a live televised broadcast, which ended by witnessing Vanguard’s explosive failure. Unfortunately, this launch mission was not ready for prime-time and occurred as a reflex reaction to the Soviet Union’s surprise aerospace success of launching the world’s first satellite, Sputnik, on October 23, 1957. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zVeFkakURXM
Vostok rocket, March 18, 1980, launched from Plesetsk, Russia (formerly the world’s busiest spaceport). While being refueled the rocket exploded on the launch pad, killing 50, mostly young soldiers. (Source: New York Times article, published September 28, 1989) http://www.nytimes.com/1989/09/28/world/1980-soviet-rocket-accident-killed-50.html
Challenger STS-51-L Space Shuttle disaster, January 28, 1986, launched from Kennedy Space Center (U.S.) marked the first U.S. in-flight fatalities. After only 73 seconds from lift-off, faulty O-ring seals failed, releasing hot gases from the solid propellant rocket booster (SRB), which led to a catastrophic failure. Seven crew members were lost, including Christy McAuliffe, selected by NASA’s Teacher in Space Program. McAullife was the first civilian to be trained as an astronaut — she would have been the first civilian to enter space, but tragically, the flight ended a short distance before reaching the edge of space. Recovery efforts for Challenger were the most expensive of any rocket launch disaster to date. http://www.history.com/topics/challenger-disaster/videos/engineering-disasters—challenger
Long Mark 3B rocket launch, payload: American communication satellite, built by Space Systems Loral – February 14, 1996 in Xichang (China) – two seconds into launch, rocket pitched over just after clearing the launch tower and accelerated horizontally a few hundred feet off the ground, before hitting a hill 22 seconds into its flight. The rocket slammed into a hillside exploding in a fireball above a nearby town, it’s estimated at least 100 people died in the resulting aftermath. This event was most likely the worst rocket launch disaster to date, due to the massive loss of human life. Disaster at Xichang | History of Flight | Air & Space Magazine http://www.airspacemag.com/history-of-flight/disaster-at-xichang-2873673/?c=y%3Fno-ist video of the rocket launch disaster ⇒ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8_EnrVf9u8s
 Delta 2, rocket launch – January 1997, Cape Canaveral (U.S.) – this rocket carried a new GPS satellite and ends in a spectacular explosion. Video link included to show examples of worst case scenario of a rocket exploding only seconds after launch (note brightly burning rocket propellant cascading to the ground is known as “firebrand”.) The short video has an interview with Chester Whitehair, former VP of Space Launch Operations Aerospace Corporation, who describes how the burning debris and toxic hydrochloric gas cloud fell into the Atlantic Ocean from the rocket explosion. Rocket launch sites and Spaceports are geographically chosen to mitigate rocket launch accidents. US rocket disasters – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y4-Idv6HnH8
Delta 2, rocket launch – January 1997, Cape Canaveral (U.S.) – this rocket carried a new GPS satellite and ends in a spectacular explosion. Video link included to show examples of worst case scenario of a rocket exploding only seconds after launch (note brightly burning rocket propellant cascading to the ground is known as “firebrand”.) The short video has an interview with Chester Whitehair, former VP of Space Launch Operations Aerospace Corporation, who describes how the burning debris and toxic hydrochloric gas cloud fell into the Atlantic Ocean from the rocket explosion. Rocket launch sites and Spaceports are geographically chosen to mitigate rocket launch accidents. US rocket disasters – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y4-Idv6HnH8
Titan 4, rocket launch – August 1998, Cape Canaveral (U.S.) the last launch of a Titan rocket – with a military, top-secret satellite payload, was the most expensive rocket disaster to date – estimated loss of $ 1.3 Billion dollars. http://www.military.com/video/explosions/blast/titan-iv-explosion-at-cape-canaveral/1137853205001/
VLS-3 rocket, launch – August 2003, Alcantara (Brazil) – rocket exploded on the launch pad when the rocket booster was accidentally initiated during test 72 hours before its scheduled launch. Reports of at least 21 people were killed at the site. http://usatoday30.usatoday.com/news/world/2003-08-22-brazil-rocket_x.htm
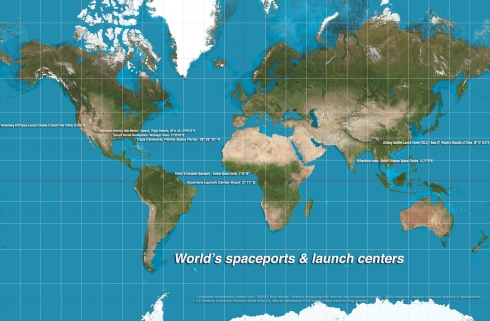
Global location & GPS coordinates of major spaceports & launch sites.
Do you see any similarities in the geographic locations of these launch sites? What advantages do these locations have regarding “Space Law?” For most rocket launches, which site has the greatest geographic advantages & why; which has the least advantages & why?
Rocket launch debris fields are color keyed in red & Links to space port’s web sites included. (CLICK ON MAP TO ENLARGE) Quiz ??? – 1.) Do you see any similarities in the geographic locations used for these launch sites? 2.) What advantages do these locations have regarding “Space Law?” 3.) For most rocket launches, which site has the greatest geographic advantage & why? 4.) Which has the least advantage & why?
Location, location, location is a huge benefit for rocket launch sites.
If you zoom into the above World map with its rocket launch sites, you’ll notice they’re located in remote, uninhabited areas. Another feature most spaceports share is their proximity to large bodies of water, which are located in an easterly direction (with the exception of the U.S. Vandenberg site.) Rockets are launched over oceans to minimize the risk to people or property from catastrophic accidents, which includes falling launch debris and toxic clouds of burnt fuel propellant. Liability from a launch vehicle is the main reason why all ships and aircraft are restricted from being in water anywhere near or underneath a rocket’s flight path. Rocket’s debris can contain highly toxic forms of unspent fuel and oxidizer, especially from solid propellant fuels.
The majority of rockets are launched in an easterly direction, due to the Earth’s easterly rotation. This procedure gives the rocket extra momentum to help escape the Earth’s gravitational pull. An exception for an east directional launch is Vandenberg site in California, which launches most of its rockets south for polar orbits used by communication and mapping satellites.
Launching rockets closer to the equator gives a launch vehicle one more advantage — extra velocity is gained from the Earth’s rotation near its equator. At the equator, our planet spins at a speed of 1675 kph (1040 mph,) compared to a spot near the Arctic Circle, which moves at a slower, 736 kph (457 mph.) Even the smallest advantage gained in velocity means a rocket requires less fuel ( 13 percent less fuel required for equatorial launches) to reach “escape velocity.” This fuel savings translates to a lighter launch vehicle, making the critical transition of leaving Earth’s gravitational field quicker.
International space law is emerging from its infancy, attempting to clearly define itself from a nebulous amalgam of; agreements, amendments, codes, rules, regulations, jurisdictions, treaties and non-binding measures. There exists today, enough legal framework for commercial interest to move cautiously towards developing outer space. However, with the unforeseen variables and dynamics of space activities, exceptions will be made & rules will be stretched, if not broken to accommodate necessity, justification or exculpation. ~
Part 1 of 2 editions – please check back soon for the conclusion of this essay.
The next edition of the Space Law series includes:
Potential Minefield Effects From Space Debris And The Regulatory Laws To Help Clean It Up.
Will Asteroid Mining Become The Next Big Gold Rush And What Laws Will Keep The Frontier Order?
Music video portal of rocket launches (nostalgia enriched content):
Boards of Canada – Dawn Chorus ⇒ http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rfVfRWv7igg
Boards of Canada – Gemini – ⇒ http://vimeo.com/68087306
Boards of Canada – Music is Math ⇒http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F7bKe_Zgk4o
Links And Resources, For Space Law And Related Issues
http://definitions.uslegal.com/s/space-law/
http://www.thespacereview.com/article/2588/1
https://www.gwu.edu/~spi/assets/docs/AGuidetoSpaceLawTerms.pdf
http://digitalcommons.unl.edu/spacelaw/38/
The Space Review: International space law and commercial space activities: the rules do apply Outlook on Space Law Over the Next 30 Years: Essays Published for the 30th … – Google Books “SPACE FOR DISPUTE SETTLEMENT MECHANISMS – DISPUTE RESOLUTION MECHANISM” by Frans G. von der Dunk Asteroid mining: US company looks to space for precious metal | Science | The Guardian Planetary Resources – The Asteroid Mining Company – News 5 of the Worst Space Launch Failures | Wired Science | Wired.com Orbital Debris: A Technical Assessment NASA Orbital Debris FAQs orbitaldebris.jsc.nasa.gov/library/IAR_95_Document.pdf A Minefield in Earth Orbit: How Space Debris Is Spinning Out of Control [Interactive]: Scientific American SpaceX signs lease agreement at spaceport to test reusable rocket – latimes.com Earth’s rotation – Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia The Space Review: Spacecraft stats and insights Space Launch Report V-2 rocket – Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Billionaire Paul Allen gets V-2 rocket for aviation museum near Seattle – Science Germany conducts first successful V-2 rocket test — History.com This Day in History — 10/3/1942
http://www.nbcnews.com/science/billionaire-paul-allen-gets-v-2-rocket-aviation-museum-near-1C9990063

























































 Radio astronomy’s powerful space exploratory telescope, was developed through research conducted by Karl Jansky in 1931. During this decade, Bell lab’s George Paget Thomson was awarded the Nobel Prize in physics for his discovery of electron diffraction, which was a key factor for solid-state.
Radio astronomy’s powerful space exploratory telescope, was developed through research conducted by Karl Jansky in 1931. During this decade, Bell lab’s George Paget Thomson was awarded the Nobel Prize in physics for his discovery of electron diffraction, which was a key factor for solid-state.














